HOSPITAL REPAIR
Repairs With Quality And Precision
Key Reasons To Have
Hospital Repair Services On A CFM56 Engine
1. Minimized Downtime:
Hospital repairs allow for significant maintenance work to be performed without the need for a full engine overhaul. By addressing specific issues in a controlled environment near the aircraft’s operating base, hospital repairs reduce the time the engine is out of service, ensuring quicker turnaround and minimizing the impact on operations.
2. Cost-Effective Maintenance:
Hospital repairs are a cost-effective solution for addressing complex issues that cannot be resolved through field service but do not require the extensive time and resources of a full overhaul. By targeting only the necessary components for repair, operators can avoid the higher costs associated with complete disassembly and shipping to a major overhaul facility.
3. Enhanced Engine Performance and Safety:
Hospital repairs focus on resolving specific issues that could affect engine performance and safety. By performing detailed inspections, repairs, and testing in a controlled environment, technicians can ensure that the engine meets all performance standards, thus extending its service life and maintaining high levels of safety.
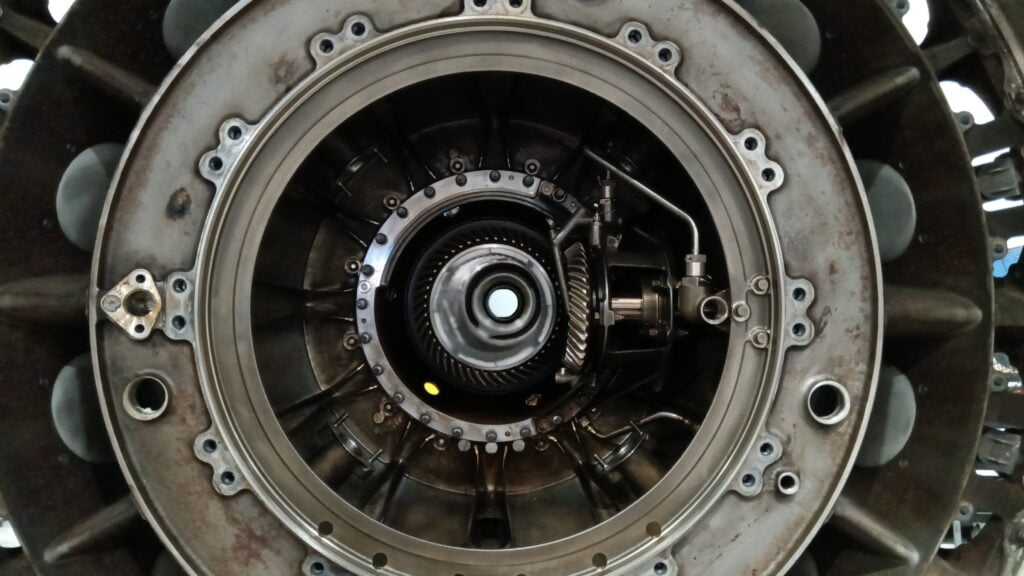

Performing hospital repairs on a CFM56 engine involves detailed procedures that require specialized knowledge and precision. “Hospital repairs” refer to more extensive maintenance tasks that are too complex for field service but do not require a full overhaul in a dedicated engine shop. These repairs typically take place in a controlled environment at or near the aircraft’s operating base. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
1. Preparation and Planning
- Assessment and Documentation: Review the engine’s service history, previous inspection reports, and any noted issues. Document the specific repairs needed, including the parts and tools required.
- Work Scope Definition: Define the scope of the repair based on the engine’s condition, including which components need to be repaired, replaced, or inspected.
2. Engine Removal (if necessary)
- Engine Shutdown: Ensure the engine is fully powered down and cool. Follow all safety protocols, including locking out power sources and draining fluids as necessary.
- Disconnection: Disconnect the engine from the aircraft, carefully labeling and documenting all connections, including electrical, hydraulic, and fuel lines.
- Transportation: Safely transport the engine to the hospital repair facility using appropriate lifting and handling equipment.
3. Engine Disassembly
- External Components Removal: Begin by removing external components, such as the nacelle, cowling, and any accessories that need to be serviced or that obstruct access to the core engine.
- Accessing the Repair Area: Disassemble the necessary sections of the engine to access the damaged or worn components. This might include removing the fan, low-pressure compressor, or turbine modules, depending on the repair scope.
- Inspection and Cleaning: Thoroughly inspect and clean the exposed areas of the engine, looking for signs of wear, corrosion, or damage that might have been missed initially.
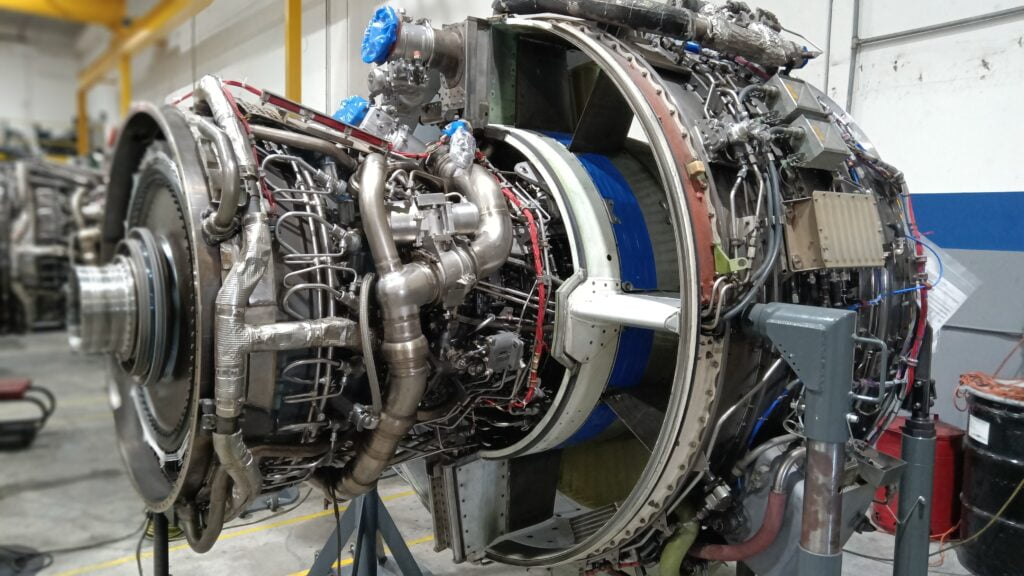
4. Component Repair and Replacement
- Non-Destructive Testing (NDT): Perform NDT techniques such as X-ray, ultrasonic, or dye penetrant testing to identify cracks, corrosion, or other structural issues.
- Repairs: Conduct the necessary repairs on identified components. This could involve welding, machining, or applying protective coatings.
- Replacement: Replace any components that are beyond repair, using manufacturer-approved parts. Ensure all parts are correctly fitted and torqued to specifications.
5. Reassembly
- Component Reinstallation: Reassemble the engine, carefully reinstalling all components in the reverse order of disassembly. Ensure all connections, such as bolts, clamps, and fittings, are secured according to the manufacturer’s specifications.
- System Checks: Reconnect electrical, hydraulic, and fuel systems. Perform continuity and pressure checks to ensure all systems are functioning correctly.
6. Final Inspection and Testing
- Visual Inspection: Conduct a detailed visual inspection to ensure there are no loose connections, foreign objects, or unaddressed issues.
- Functional Testing: Run diagnostic tests to verify the functionality of repaired components. This may include spin tests, pressure checks, and verifying clearances.
- Engine Run-Up (if applicable): If required, perform an engine run-up test to ensure it operates correctly under load. Monitor all parameters, including temperature, vibration, and pressure, to confirm that the engine is performing to standard.
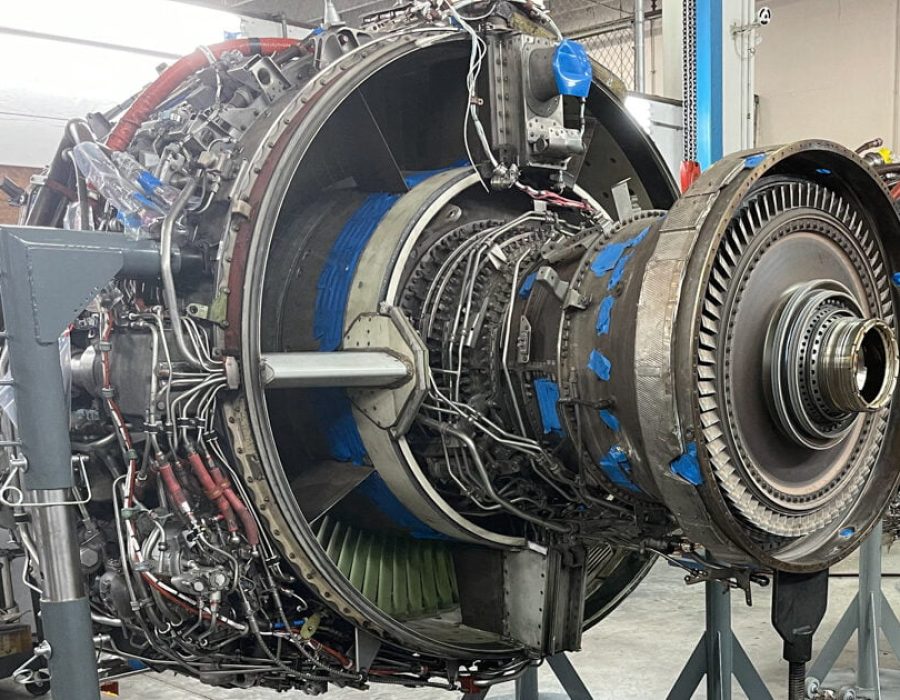

7. Documentation and Certification
- Record Keeping: Document all repairs, inspections, and tests performed during the hospital repair. Include details of parts used, test results, and any deviations from the standard procedures.
- Certification: Ensure that all repairs are certified by a licensed technician and that the engine meets regulatory and manufacturer standards before returning it to service.
8. Reinstallation (if engine was removed)
- Transport Back to Aircraft: Safely transport the repaired engine back to the aircraft.
- Reinstallation: Reinstall the engine, reconnecting all systems according to documented procedures.
- Final Checks: Perform a final set of checks to ensure all connections are secure, and systems are operational.
9. Return to Service
- Ground Testing: Perform any required ground testing, including engine run-ups, to ensure everything is functioning correctly.
- Approval: Obtain final approval from the quality assurance team or an authorized inspector before releasing the engine back into service.
- Documentation Submission: Submit all repair records and certifications to the appropriate regulatory authorities and maintain copies for future reference.
This detailed process ensures that the CFM56 engine is repaired to the highest standards, maintaining its performance, safety, and reliability.
Got questions? We’ve got answers.
